Please specify the quantity of product(s).


Loading...
ITEM: 57820
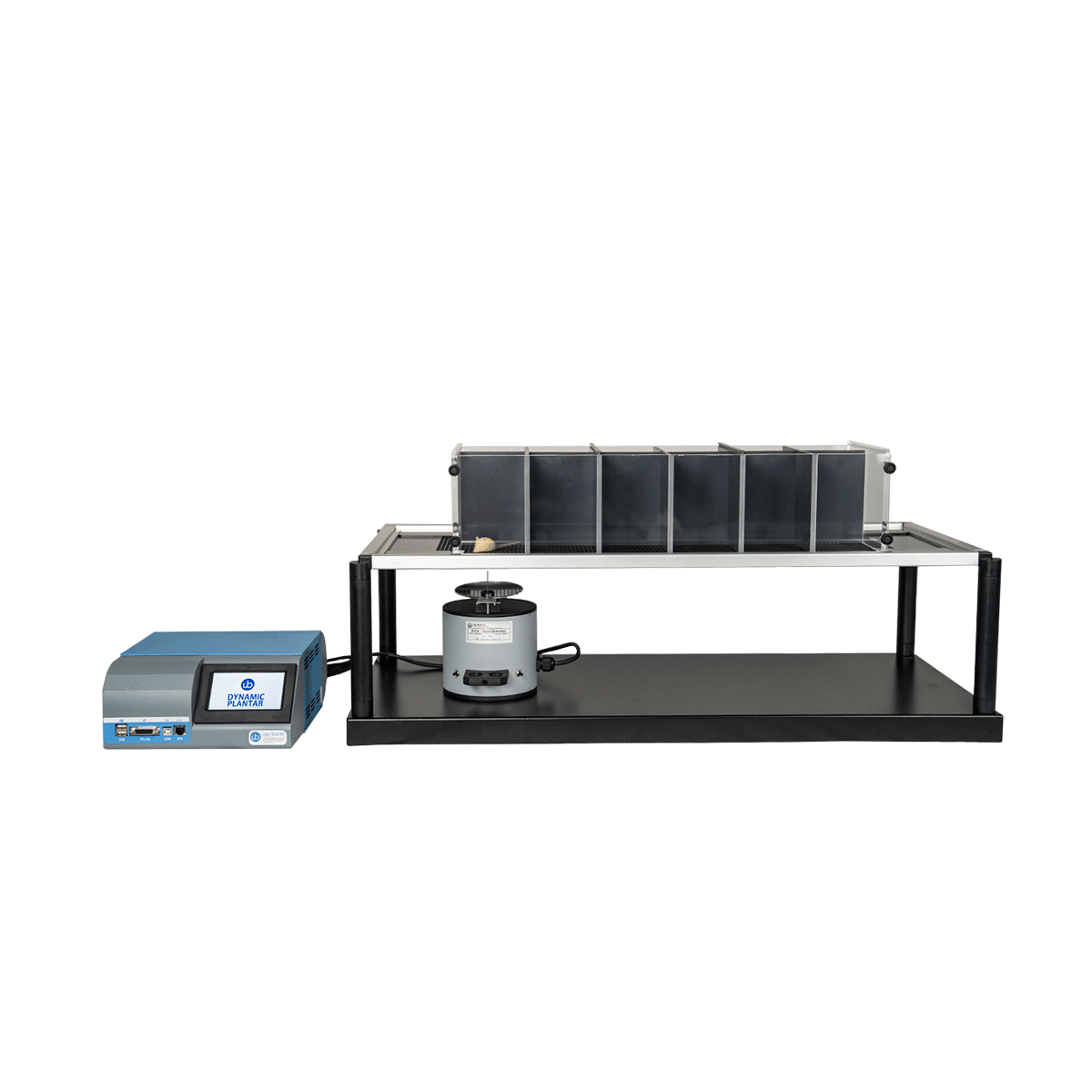
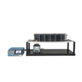
Ugo Basile Dynamic Plantar
For assessment of hypersensitivity and allodynia for analgesia, nociceptive, neuropathic and postsurgical studies.
| Item | Product | Price | QTY |
|---|---|---|---|
| 57820 | Ugo Basile Dynamic Plantar (Von Frey) | Login | |
| 57816 | Ugo Basile Grid Platform for Plantar Stimulation | Login | |
| 57824 | Multiple Configuration Animal Enclosure (3-12 Animals) | Login | |
| 57829 | Spare Filament for Dynamic Plantar | Login | |
| 57829-4 | Dynamic Plantar Filament, 0.4mm | Login | |
| 57829-3 | Dynamic Plantar Filament, 0.3mm | Login |
The Ugo Basile Dynamic Plantar Aesthesiometer has been designed to automate the assessment of “touch sensitivity” on the plantar surface of rats or mice and comes ready to work with both Mice and Rats. It is known by some as the Electronic Von Frey or Plantar Von Frey instrument, but it differs from Von Frey devices as Latency and Actual Force at the time of paw withdrawal reflex are automatically detected and recorded.
Background
- The automated Dynamic Plantar Aesthesiometer (DPA) is a quick, accurate way of delivering mechanical stimulation and measuring a response.
- Impaired cutaneous sensation is usually first manifested in a loss of light touch detection. Mechanical stimulation is used clinically to diagnose pathologies of hyper- or hypo-aesthesia, brought about by drugs, neural pathology or experimental lesions.
Application & Disease Models
- Automatically detects and records latency time, and actual force at the time of paw withdrawal reflex.
- A movable force actuator is positioned below the plantar surface of the animal. The desired force and force speed (ramp) is applied, as pre-set by the operator.
- Increasing force is exerted by rigid Von Frey filament (0.5mm tip) until the animal twitches its paw.
- Adjustable touching force and touching pause (to control the stimulus approaching phase).
- Paw withdrawal detection is automatic. Manual detection is also available (useful if animal motor response is unusual).
- The device comprises:
- A movable touch-stimulator unit complete with filament actuator and adjustable angled-mirror
- A microprocessor controlled electronic unit with touch screen, graphic display, internal memory for data storage, USB key and optional printer
- Large testing surface (perforated metal platform), laser cut for smooth and precise grid spacing
- Modular animal enclosure offering from 3 to 12 spaces is convenient for holding rats and mice
- Supplied with accessories to work with both mice and rats.
- Data can be transferred to a computer via the memory stick.
- TTL outputs for Start/Stop and Detection (Manual/Automatic) as well as TTL Input for external start provide easy interface to external instruments such as DAQs. Analog output is also available.
Impaired cutaneous sensation is usually first manifested in a loss of light touch detection. So “mechanical” stimulation has a long history of effective clinical use to diagnose pa-thologies of hyper- or hypo-aesthesia, brought about by drugs, neural pathology or experimental lesions, etc.
The Dynamic Plantar Aesthesiometer was developed to apply a reproducible light touch to the rodent plantar surface, and quantify the force which causes the animal to react by withdrawing the paw.
| BASIC | |
| Starting | By Start button, push buttons or TTL input |
| Stopping | By Stop button, push buttons, cut-off or TTL input |
| Force range | 0.1 to 100 grams, in 0.1g steps |
| Force increasing rate | Adjustable in the interval 0 to 50 seconds, in 1 s steps |
| Filament travel | 12 mm |
| Latency time | Display in 0.1s steps |
| TTL/IO | Start/Stop, Detection Mode, Force level |
| Data export | .csv format |
| PHYSICAL | |
| Universal Mains | Universal input 100-240 VAC, 50-60 Hz, 30W |
| Total Weight | Kg. 10.20 |
| Shipping Weight | Kg. 18.50 approx. |